What are the Three Main Types of Accounts: A Clear Overview

It does not provide a real-time view of a company’s financial position, and it may not be suitable for complex financial transactions. In addition, it requires a significant amount of manual work, which can be time-consuming and prone to errors. Accounts payable is a type of liability account that records the company’s obligations to its suppliers.
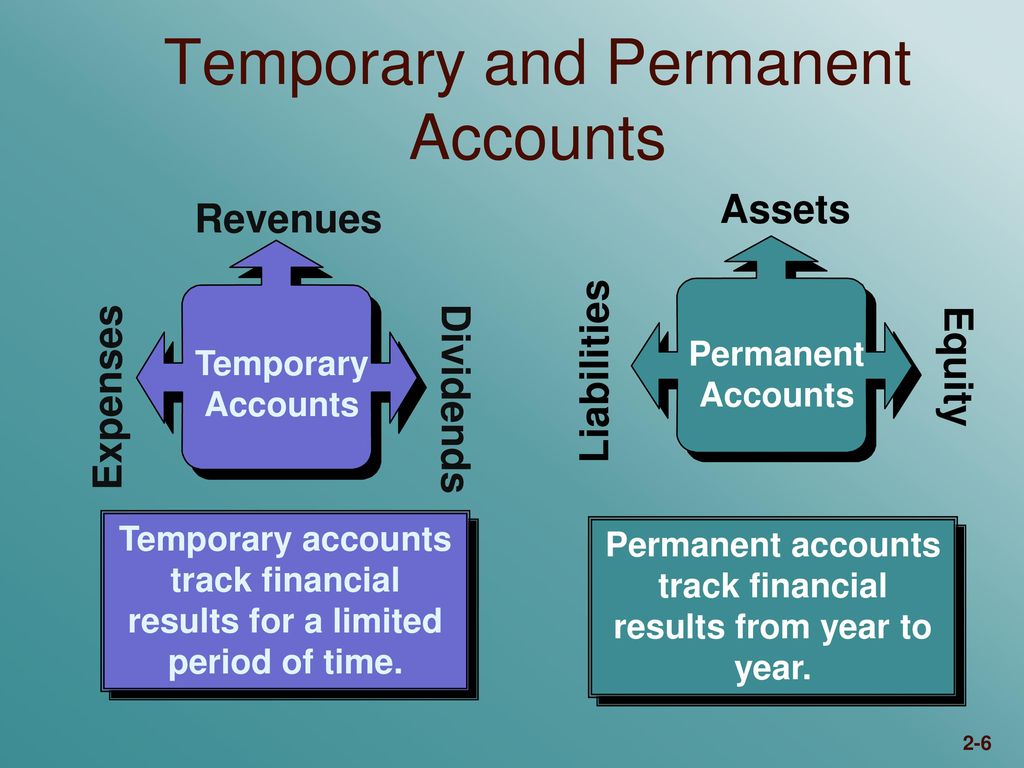
Permanent accounts vs temporary accounts
This means that the balances in these accounts are transferred to the income statement, where they are used to calculate the net income or net loss of the business. These accounts track the owner’s residual interest in the company after liabilities are deducted from assets. which of the following accounts are permanent Equity accounts accumulate over time, reflecting the long-term financial health and ownership structure of the business. Also known as real or general ledger accounts, the accountants record the closing balance of the permanent account at the end of the accounting period.
What are the three main types of accounts in business?
Automated systems can generate and post closing entries, transfer balances to permanent accounts, and prepare the necessary financial reports with minimal manual intervention. At the end of an accounting period, the balance in a temporary account is not carried forward. Any remaining balance is then transferred to a permanent account, which typically involves the retained earnings on the balance sheet. This resets the temporary account balance to zero at the beginning of the next fiscal period. Unlike temporary accounts, permanent accounts are not closed at the end of the accounting period. For example, the balance of Cash in the previous year is carried onto the next year.
Sales
Inventory accounts represent the stock of goods that a business holds for sale. These accounts are used to record the cost of goods sold and the cost of goods remaining in stock. Building, land, equipment, and furniture accounts represent the fixed assets of a business. Liabilities are obligations that a company owes to others, such as loans or unpaid bills. They are also listed on a company’s balance sheet and are categorized as either current or non-current liabilities. Real accounts also consist of contra assets, liability, and equity accounts.
What are the three parts of an accounting system?
Revenue accounts are used to record the income earned by a business, while expense accounts are used to record the costs incurred by a business. The balance of these accounts can increase or decrease depending on the inflow or outflow of cash. Artificial personal accounts are accounts that are maintained for entities that are not individuals. These accounts include accounts of entities such as trusts, clubs, associations, and so on. Automation minimizes human error by ensuring that transactions are recorded accurately in both temporary and permanent accounts.
Revenue accounts
For both temporary and permanent accounts, this means that any discrepancies or anomalies can be identified and addressed quickly, reducing the risk of inaccurate financial reporting. One of the most significant challenges businesses face when managing temporary and permanent accounts is ensuring they are accurately recorded. Any errors in recording can lead to inaccurate financial statements, which can have severe consequences. Accurate recording is essential for businesses to make informed financial decisions and maintain credibility. At year-end, you carry over your permanent accounts that are now your retained earnings into the new year.
Our solution has the ability to prepare and post journal entries, which will be automatically posted into the ERP, automating 70% of your account reconciliation process. Uncover why real-time data is essential for an efficient continuous close process. Because you did not close your balance at the end of 2021, your sales at the end of 2022 would appear to be $120,000 instead of $70,000 for 2022. Investments can be a valuable source of income for businesses, but they also come with risks. The value of investments can fluctuate based on market conditions, and businesses must be prepared to weather these ups and downs.
Whether you’re just starting your business or you’re already well on your way, keeping organized financial records is a must. Download our FREE whitepaper, How to Set up Your Accounting Books for the First Time, for the scoop. The assumption is that all income from the company in one year is held onto for future use.
- As a result, when the new accounting period begins, the account maintains the closing balance from the preceding period.
- In this blog, we’ll explore the key differences between temporary and permanent accounts and understand the key role they play in ensuring accurate financial reporting.
- By tracking the money that is coming in, a business can determine whether it is profitable and make decisions about how to allocate resources.
- If at the end of 2020 the company had Cash amounting to $100,000, that amount will be carried as the beginning balance of cash in 2021.
If no transactions are ever recorded that involve such an account, or if the balance has been zeroed out, a permanent account may contain a zero balance. Bank accounts and checking accounts are typically included in the chart of accounts. Bank accounts are used to track money that is held in a bank, while checking accounts are used to track money that is spent or received through checks. Expense accounts are typically organized by category, such as office expenses, travel expenses, or advertising expenses. Each category may have its own sub-accounts, which are used to track specific expenses within that category. Common stock is a type of equity that represents ownership in a company.
The three parts of an accounting system are recording, classifying, and summarizing. Effective management of customer and debtor accounts is critical to the financial health of a business. They are used to provide more detail about a specific transaction or to track transactions for a specific project or department. For example, a company might have a general account for office supplies, but create sub-accounts for paper, pens, and other specific items.

