What Are Assets, Liabilities, and Equity?
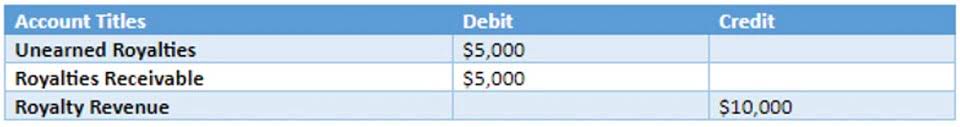
These include liabilities whose amount can be determined, liabilities that represent collections for third parties or depend upon operations, and contingent liabilities. Let us take a closer look at each of these current liabilities types. This means that the total value of current liabilities shows how much revenue and cash a company needs to generate in the short term to cover its dues. Current liabilities are listed on the right side of the balance sheet under the “Liabilities” section, from the shortest-term to the longest-term. Most balance sheets will include a separate section for long-term or non-current liabilities – those that must be settled in more than one year. All this information is summarized on the balance sheet, one of the three main financial statements (along with income statements and cash flow statements).
How Do Investors Use Noncurrent Liabilities?
- Similarly, business owners and managers can use the current liabilities to evaluate the financial health of their company and plan for the future.
- Using accounting software can help ensure that each journal entry you post keeps the formula in balance.
- Liability may also refer to the legal liability of a business or individual.
- The type of equity that most people are familiar with is “stock”—i.e.
- An expense is the cost of operations that a company incurs to generate revenue.
A liability, like debt, can be an alternative to equity as a source of a company’s financing. Moreover, some liabilities, such as accounts payable or income taxes payable, are essential parts of day-to-day business operations. Long-term liabilities or debts are the money a company owes to third-party creditors that must be repaid in longer than twelve months. The Current Portion of Long-Term Debt (CPLTD) is the amount of unpaid principal from long-term debt that has accrued during a company’s normal operating period (usually less than twelve months). This amount must be paid in that time period and is, therefore, considered a current liability.

Want More Helpful Articles About Running a Business?
In general, a liability is an obligation between one party and another not yet completed or paid for in full. Current liabilities on the balance sheet must be calculated and managed prudently to ensure that the company has sufficient current assets to cover the dues. Many companies are responsible to cover payroll liabilities that are due within one year. These are the payroll expenses that a business owes but has not yet paid; many of these expenses will appear every time a business runs payroll. Depending on the company and its industry, you will see many kinds of items listed under other current liabilities.
Types of Liability Accounts – Examples
Here’s a simplified version of the balance sheet for you and Anne’s business. Right after the bank wires you the money, your cash and your liabilities both go up by $10,000. If you’ve promised to pay someone in the future, and haven’t paid them yet, that’s a liability. Accounts that require greater transparency often become a single line item, and accounts that are not essential to a firm’s core operations may be grouped together as “other.” Like assets, liabilities may be classified as either current or non-current.
Having a successful business doesn’t mean that you have expert bookkeeping skills. Enlist personal expert support from a competent bookkeeping service like Fincent to see to the what falls under liabilities accounts side while you focus on what you know best about your business. When the art gallery entered into its second year, Amrish hired the services of a bookkeeping service.
Examples of Liabilities

Similarly, Accounts Payable are current liabilities, while Accounts Receivable are current assets. The Cash Ratio is another liquidity measure showing the company’s ability to cover its short-term obligations. It can be calculated by finding the total cash and cash equivalents and dividing the result by current liabilities. The Quick Ratio calculation is similar to the Current Ratio calculation, except that the value of inventories is subtracted beforehand.
- A lower debt ratio indicates more capacity of a business to pay off its debts.
- Let us take a closer look at each of these current liabilities types.
- A contingent liability is an obligation that might have to be paid in the future but there are still unresolved matters that make it only a possibility, not a certainty.
- The current ratio measures a company’s ability to pay its short-term financial debts or obligations.
- These could be any number of outstanding payments, like bills, taxes, loans, or any payment for goods and services rendered by third parties.
- Or the business’s leaders (CFO, Controller, etc.) may set restrictions themselves to ensure they have enough working capital available.
Liabilities vs. Expenses
It tells you when you’ve made a mistake in your accounting, and helps you keep track of all your assets, liabilities and equity. Using other current liabilities as a category is standard practice and does not need the level of review often seen with off-balance sheet items. Capital refers to the net interest in the company and is equal to total assets minus total liabilities. A. Current liabilities – A liability is considered current if it is due within 12 months after the end of the balance sheet date.
As such, they use ratios based on the value of current liabilities, such as Current and Quick Ratios, to analyze a company’s solvency and overall financial position. Long-term liabilities are financial obligations of a company that extends more than a year. These liabilities affect a company’s financial structure because they indicate the amount of debts you have acquired to finance your assets and business operations. Accrued expenses are listed in the current liabilities section of the balance sheet because they represent short-term financial obligations. Companies typically will use their short-term assets or current assets such as cash to pay them. Current liabilities of a company consist of short-term financial obligations that are typically due within one year.
- Accounts payable would be a line item under current liabilities while a mortgage payable would be listed under long-term liabilities.
- This funding helps businesses generate cash flow and purchase equipment to speed up their production process.
- Financial liabilities can be either long-term or short-term depending on whether you’ll be paying them off within a year.
- The balance sheet is one of three financial statements that explain your company’s performance.
- Liability is the money that a business owes a financial institution.

