Material Variances Formula, Calculation, Examples, and FAQs

The net direct materials cost variance is still $1,320 (unfavorable), but this additional analysis shows how the quantity and price differences contributed to the overall variance. Because the company uses 30,000 pounds of paper rather than the 28,000-pound standard, it loses an additional $20,700. Like direct materials price variance, this variance may be favorable or unfavorable. If workers manufacture a certain number of units using a quantity of materials that is less than the quantity allowed by standards for that number of units, the variance is known as favorable direct materials quantity variance. On the other hand, if workers use the quantity that is more than the quantity allowed by standards, the variance is known as unfavorable direct materials quantity variance.
Journal Entries for Accounting Investments in Subsidiaries
Total actual and standard direct materials costs are calculated by multiplying quantity by price, and the results are shown in the last row of the first two columns. When complete, capitalizable variances should be recorded in a “standard-to-actual” reserve within inventory on the balance sheet with the remainder being appropriately expensed through the income statement. This reserve has the effect of adjusting the company’s inventory balances to “actual,” which is appropriate under GAAP. On a net basis, the purchase price variance is really the difference between standard cost of the material and the actual invoice price of the material.
Do you own a business?
Understanding the factors that influence direct material variance is essential for businesses aiming to maintain control over their production costs. Market conditions, geopolitical events, and changes in supply and demand can all cause fluctuations in material costs. For instance, a sudden increase in the price of steel due to international trade policies can lead to an unfavorable material price variance for manufacturers relying on this resource. Companies must stay informed about market trends and consider strategies such as hedging or long-term contracts to mitigate these risks. With our direct material price variance calculator, we aim to help you assess the difference between the actual cost of direct materials and the standard cost.
Example of Direct Materials Quantity Variance
To calculate direct materials, add beginning direct materials to direct materials purchases and subtract ending direct materials. For example, say that a company had $3,000 worth of flour stock at the beginning of the year, bought $10,000 worth of flour during the year, and has $2,000 worth of flour goods and services definition remaining at year end. We compared standard cost to the ability of a household to budget food costs for a month. Through this, we saw how it acts both as a guideline for appropriate spending habits for those who may not purchase routinely, as well as a better way to plan for future spending.
- The direct materials quantity variance is one of the main standard costing variances, and results from the difference between the standard quantity and the actual quantity of material used by a business during production.
- Conversely, issues such as late deliveries, substandard materials, or unexpected price hikes can lead to variances.
- Remember that a standard cost is the amount that you expect to pay for a good or service, especially when it comes to creating something.
- The difference between the expected and actual cost incurred on purchasing direct materials, expressed as a positive or negative value, evaluated in terms of currency.
The materials price variance can be computed either when materials are purchased or when they are placed into production. The standard rates calculated for batch and product level activities do not vary with production volume. This example illustrates the accounting entries for purchase price variance and exchange rate variance for a standard cost item.
How can businesses improve their direct material price variance?
This is the difference between the standard and actual cost per unit of the direct materials purchased, multiplied by the standard number of units expected to be used in the production process. To calculate the direct material quantity variance, we measure the difference between the standard cost of materials that should have been used to produce the actual level of output and the standard cost of the actual quantity of materials used. If a company’s actual quantity used exceeds the standard allowed, then the direct materials quantity variance will be unfavorable. This means that the company has utilized more materials than expected and may have paid extra in materials cost.
However, the initial calculation provides a broad overview that can guide more detailed analysis. By regularly monitoring these variances, businesses can quickly identify trends or anomalies that may indicate underlying issues, such as supplier problems or inefficiencies in the production process. $10 times 1000 units creates a $10,000 unfavorable variance for labor, since it costs you more money.
He has been a manager and an auditor with Deloitte, a big 4 accountancy firm, and holds a degree from Loughborough University. A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation. The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice. All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly. 11 Financial may only transact business in those states in which it is registered, or qualifies for an exemption or exclusion from registration requirements. 11 Financial’s website is limited to the dissemination of general information pertaining to its advisory services, together with access to additional investment-related information, publications, and links.
Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs. For information pertaining to the registration status of 11 Financial, please contact the state securities regulators for those states in which 11 Financial maintains a registration filing. Dummies has always stood for taking on complex concepts and making them easy to understand. Dummies helps everyone be more knowledgeable and confident in applying what they know.
The actual quantity (1,200 sheets) of plastic is removed from the raw materials inventory at the standard price (4.00) giving a credit entry of 4,800 posted to the account. The standard quantity (1,000) which should have been used in production is transferred to work in process inventory at the standard price (4.00), giving a total debit entry of 4,000. The difference between the two postings is the variance of -800, which is posted to the direct materials variance account as a debit representing the unfavorable variance. The difference in the quantity is multiplied by the standard price to determine that there was a $1,200 favorable direct materials quantity variance.
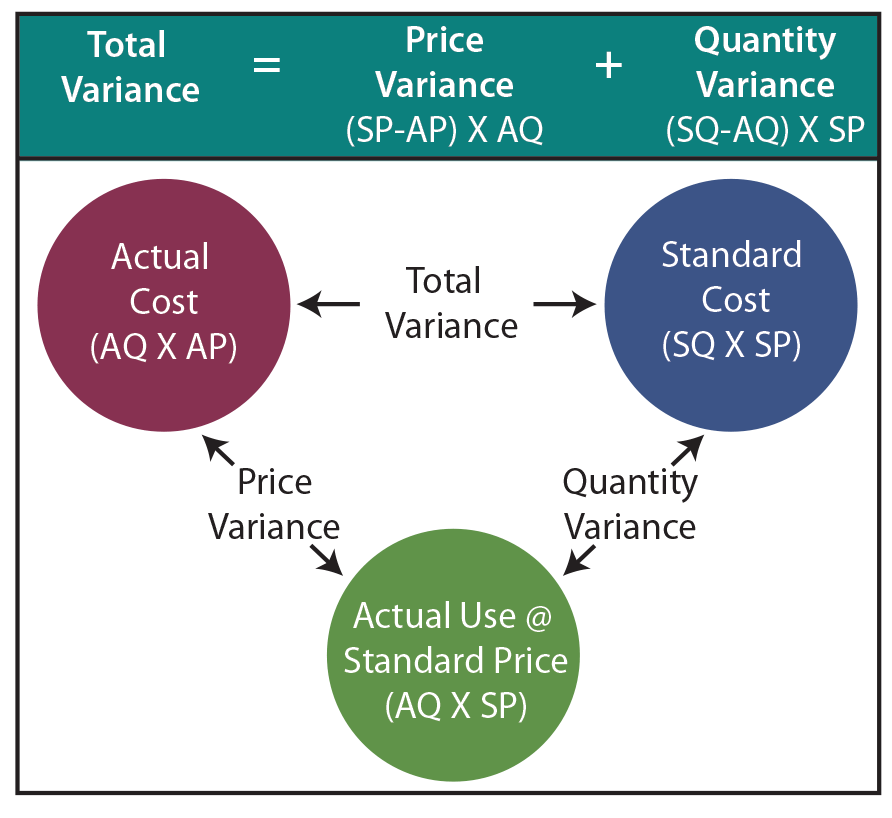
Additionally the variance is sometimes referred to as the direct materials usage variance or the direct materials efficiency variance. It is usually better to compute the variance when materials are purchased because that is when the purchasing manager, who has responsibility for this variance, has completed his or her work. In addition, recognizing the price variance when materials are purchased allows the company to carry its raw materials in the inventory accounts at standard cost, which greatly simplifies bookkeeping. The material price variance calculation tells managers how much money was spent or saved, but it doesn’t tell them why the variance happened. One common reason for unfavorable price variances is a price change from the vendor. Companies typically try to lock in a standard price per unit for raw materials, but sometimes suppliers raise prices due to inflation, a shortage or increasing business costs.

