OBEX Securities Investments
Rather, most dilutive securities provide a mechanism through which the owner of the security can obtain additional common stock. If triggering the mechanism results in a decreased EPS for existing shareholders—by increasing the total amount of outstanding shares—then the instrument is said to be a dilutive security. Dilution occurs when a company issues new shares that result in a decrease in existing stockholders’ ownership percentage of that company. Stock dilution can also occur when holders of stock options, such as company employees, or holders of other optionable securities exercise their options. When the number of shares outstanding increases, each existing stockholder owns a smaller, or diluted, percentage of the company, making each share less valuable. Some examples of dilutive securities include convertible preferred stock, convertible debt instruments, warrants, and stock options.
Impact of Fully Diluted EPS on Stock Valuation
Adam received his master’s in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
How confident are you in your long term financial plan?
In the end, acquiring capital through a secondary offering can be a longer-term positive for the investor, if the company becomes more profitable and the stock price rises. If a company has a total of 1,000 shares of float on the market, for example, and its management issues another 1,000 shares in a secondary offering, there are now 2,000 shares outstanding. This means that an owner of 100 shares now owns 5% of the company rather than 10%.
Create a Free Account and Ask Any Financial Question
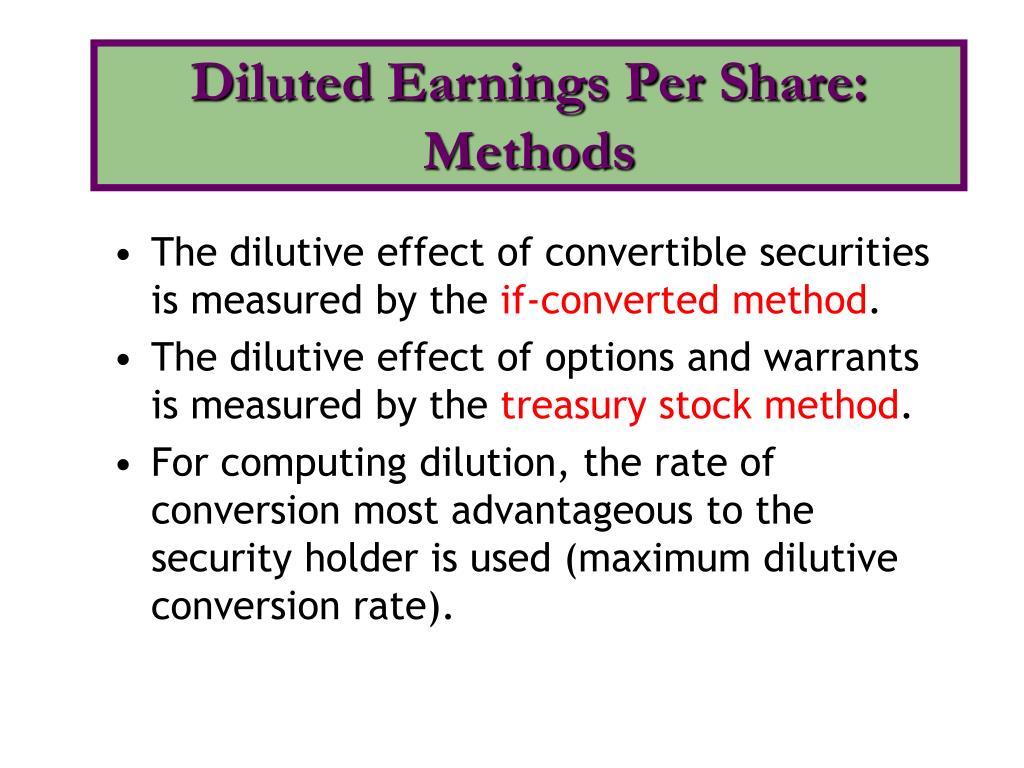
- By owning convertible bonds, the owners can convert them into common stock.
- A company must make adjustments to its earnings per share and ratios for its valuation when dilution occurs.
- For this reason, many public companies publish estimates of both non-diluted and diluted EPS, which is essentially a “what-if-scenario” for investors in the case new shares are issued.
- It takes into account all potential dilutive securities that could convert into common stock and affect the number of outstanding shares.
In certain cases, investors with a large chunk of stock can often take advantage of shareholders that own a smaller portion of the company. Suppose the company then issues 10 new shares and a single investor buys them all. There are now 20 total shares outstanding and the new investor owns 50% of the company. Meanwhile, each original investor now owns just 5% of the company—one share out of 20 outstanding—because their ownership has been diluted by the new shares.
Assumptions and Estimates in the Calculation
Since many companies have obligations that could result in additional shares being issued, it is best to express financial metrics such as EPS using a diluted share count. Dilution protection provisions are generally found in venture capital funding agreements. Dilution protection is sometimes referred to as “anti-dilution protection.” In addition to information about significant accounting practices and tax rates, footnotes usually describe what factored into the diluted EPS calculation. The company may provide specific details regarding stock options granted to officers and employees and their effects on reported results. The Treasury stock method is used to calculate diluted EPS for potentially dilutive options or warrants.
Dilutive Securities vs. Anti-Dilutive Securities: What’s the Difference?
It has an issue of preferred stock on which it paid $1,000,000 of dividends, and which is convertible to 400,000 common shares. The preferred stock is not considered to be equivalent to the common stock. Fully diluted EPS is important for investors, analysts, and companies to assess the impact of various 8 stylist secrets for healthy, shiny hair securities on the company’s earnings per share. It is also useful for comparing companies in the same industry and can impact the stock valuation of a company. If the company then has a secondary offering and issues 100 new shares to 100 more shareholders, each shareholder only owns 0.5% of the company.

For example, each $1,000 of convertible debt may convert to 100 shares of common stock, thus decreasing current stockholders’ total ownership. The if-converted method is used to calculate diluted EPS if a company has potentially dilutive preferred stock. To use it, subtract preferred dividend payments from net income in the numerator and add the number of new common shares that would be issued if converted to the weighted average number of shares outstanding in the denominator. Convertible preferred stock is often issued to investors who want the benefits of owning a preferred share with the security that it can be turned into a common share at any time. These shares work in many different ways, but the most common convertible preferred shares can be converted for a set amount of common shares upon demand of the shareholder.
These calculations involve bringing in the savings and new shares in order from the most to the least dilutive. Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications. Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others. Finance Strategists is a leading financial education organization that connects people with financial professionals, priding itself on providing accurate and reliable financial information to millions of readers each year. Our team of reviewers are established professionals with decades of experience in areas of personal finance and hold many advanced degrees and certifications. 11 Financial may only transact business in those states in which it is registered, or qualifies for an exemption or exclusion from registration requirements.
If all convertible securities of a corporation are exercised, all of these securities and extra shares are included in the fully diluted shares. You can also acquire warrants at a specific price and during a specified period/time. The only difference between the warrants and the options is the parties they’re being issued to. The company issues Options to the employees, whereas the company issues warrants to the individuals outside the company. If converted, dilutive securities effectively increase the weighted number of outstanding shares, decreasing EPS, and thereby devaluing a shareholder’s existing equity stake.
Understandably, share dilution is not often viewed favorably by existing shareholders, and companies sometimes initiate share repurchase programs to help curb the effects of dilution. In situations where a company splits its stock, current investors receive additional shares while the price of the shares is adjusted accordingly, keeping their percentage ownership in the company static. Antidilutive activities maintain or increase the voting power or EPS for existing shareholders by lowering the company’s outstanding share count or increasing the company’s earnings. It also becomes more difficult to determine the number of shares outstanding at a given time as more security types are introduced. These are common with convertible preferred stock, which is a favored form of venture capital investment. To calculate diluted EPS, include the number of dilutive shares, or the number of shares that would exist if all of a company’s existing potential share obligations were exercised, in the weighted average with the outstanding common shares.
Antidilutive refers to activities that maintain or increase EPS and shareholder voting power. Conversely, dilutive describes the effect of certain actions or activities that reduce EPS. As a result of dilutive activities, existing shareholders’ ownership interests are reduced. Convertible equity is often called convertible preferred stock and usually converts to common stock on a preferential ratio.

